Last Updated on February 17, 2026 by Ian Naylor
Unnatural links can destroy your site’s search rankings. If Google flags your site for manipulative backlinks, your traffic can drop by over 90%, and recovery is slow and challenging. Here’s what you need to know:
- Unnatural links include paid links, link exchanges, automated schemes, and over-optimized anchor text.
- Google penalties come in two forms: manual actions (issued by human reviewers) and algorithmic devaluations (like Penguin or SpamBrain).
- Key risks: Sites with unnatural links may lose rankings, traffic, and even visibility in search results.
- How to fix it: Audit your backlinks, remove or disavow harmful links, and build high-quality, relevant links instead.
To avoid penalties, focus on earning links naturally through valuable content and ethical practices. Regularly monitor your backlink profile and act quickly if issues arise. Google’s SpamBrain is more advanced than ever – manipulative tactics that worked in the past won’t work now.
Manual Actions: Unnatural Links To Your Site – How To Fix & What To Do
sbb-itb-88880ed
The Risks of Unnatural Links
Unnatural links can wreak havoc on your site’s visibility and traffic, thanks to both automated penalties and manual actions from Google. If manipulative linking patterns are detected, the consequences can be severe. Knowing the differences between these penalties is essential for crafting an effective link-cleanup plan and staying on Google’s good side.
Algorithm Penalties: Penguin and Spam Updates
Google’s Penguin algorithm is designed to automatically identify unnatural links. Unlike manual penalties, Penguin doesn’t send out notifications – you’ll only notice its effect when your rankings take a sudden nosedive.
Penguin flags two major red flags: over-optimized anchor text (e.g., hundreds of backlinks using the exact same keyword) and links from spammy or low-quality domains. If Penguin catches these patterns, it might devalue those links – or worse, lose trust in your entire site. Google’s Gary Illyes has explained the potential fallout:
"If Penguin sees signs of manipulation, it can decide to discount ALL the links, which can be pretty bad for a site".
In extreme cases, a strong pattern of manipulative links can lead Google’s algorithms to distrust your entire domain. This loss of trust can result in sitewide ranking drops, not just penalties for specific pages.
Since Penguin 4.0, Google focuses more on ignoring problematic links rather than outright penalizing sites. However, severe manipulation can still cause significant visibility issues. John Mueller from Google emphasizes this risk:
"If our systems recognize that they can’t isolate and ignore these links across a website, if we see a very strong pattern there, then it can happen that our algorithms say well we really have kind of lost trust with this website… and then you can see kind of a drop in the visibility there".
Recovering from an algorithmic penalty involves cleaning up your backlink profile and waiting for Google to recrawl and reevaluate your site. Unlike manual actions, there’s no formal reconsideration request for these penalties.
Manual Actions and Their Effects
Manual actions are penalties issued by human reviewers at Google. If your site violates Google’s spam policies, you’ll be notified directly in the "Manual actions" report within Google Search Console. These penalties can target specific pages or directories, or they can be sitewide, impacting your entire domain.
The effects of manual actions can range from noticeable ranking drops to complete removal from Google’s index. Affected pages might vanish entirely from search results. As Google explains:
"If a site has a manual action, some or all of that site will not be shown in Google search results".
Recovering from a manual action isn’t automatic. You’ll need to clean up your backlink profile, document your efforts, and submit a formal reconsideration request to Google. Even after the penalty is lifted, your traffic might not fully recover because the unnatural links that were artificially boosting your rankings are no longer in play. Unlike algorithmic penalties, manual actions require explicit human approval for resolution.
How to Find Unnatural Links on Your Site
To identify unnatural links on your site, you’ll need a combination of automated tools and manual investigation. This process helps uncover patterns and warning signs that point to manipulative linking practices.
Warning Signs of Unnatural Links
Here are some key indicators that a link might be unnatural:
- Over-optimized Anchor Text: If you notice clusters of identical keyword phrases in anchor text, it’s a strong signal of manipulation. Organic links usually show more variety in anchor text usage .
- Low Domain Authority: A large number of links coming from sites with low Domain Ratings often signals participation in link schemes .
- Irrelevant Context: Links from sites with no topical relevance – like a gambling site linking to a children’s education platform – are a major red flag .
- Spammy Source Types: Watch out for links from low-quality directories, automated forum signatures, blog comment spam, or Private Blog Networks (PBNs). For instance, Overstock faced a ranking penalty in 2011 when Google uncovered a scheme where the company offered discounts in exchange for embedding links on university (.edu) websites using exact-match anchors like "bunk beds" and "gift baskets" .
- Unnatural Placement: Links hidden through CSS, disguised as plain text, or embedded in sitewide footers and sidebars without editorial oversight are classic signs of manipulation .
- Rapid Link Acquisition: A sudden spike in backlinks, especially from a single domain, can indicate an attempt to artificially boost PageRank.
Spotting these red flags is just the starting point for identifying problematic links. A detailed audit will help you dig deeper into your backlink profile and identify opportunities for link diversification.
Tools for Auditing Your Backlinks
Once you’ve identified potential warning signs, turn to auditing tools for a more thorough analysis. Start with Google Search Console. Check the "Manual Actions" report under "Security & Manual Actions" to see if Google has flagged your site for unnatural links .
For deeper insights, these tools can be invaluable:
- Semrush‘s Backlink Audit: This tool evaluates links using over 45 toxic markers. It categorizes backlink profiles as highly toxic (10% or more flagged links), medium toxic (3–9%), or low toxic (under 3%).
- Ahrefs: Its Anchors Report and Domain Rating (DR) metric help identify over-optimized anchor text and low-authority domains .
- Moz: Moz’s Spam Score predicts whether a domain might be penalized or banned based on various site features.
These tools rely on proprietary metrics like Toxicity Score (TS), Domain Rating (DR), and Spam Score to pinpoint harmful links. Focus your attention on links with a Toxicity Score of 60 or higher, as these usually require immediate review or removal.
However, automated tools aren’t foolproof. Even the best tools can mislabel safe links as harmful. To ensure accuracy, manually review a sample of about 20 linking pages. Look for signs of natural integration into the content or links hidden in footers and widgets. A manual review adds an extra layer of confidence to your audit process.
How to Remove Unnatural Links and Avoid Penalties
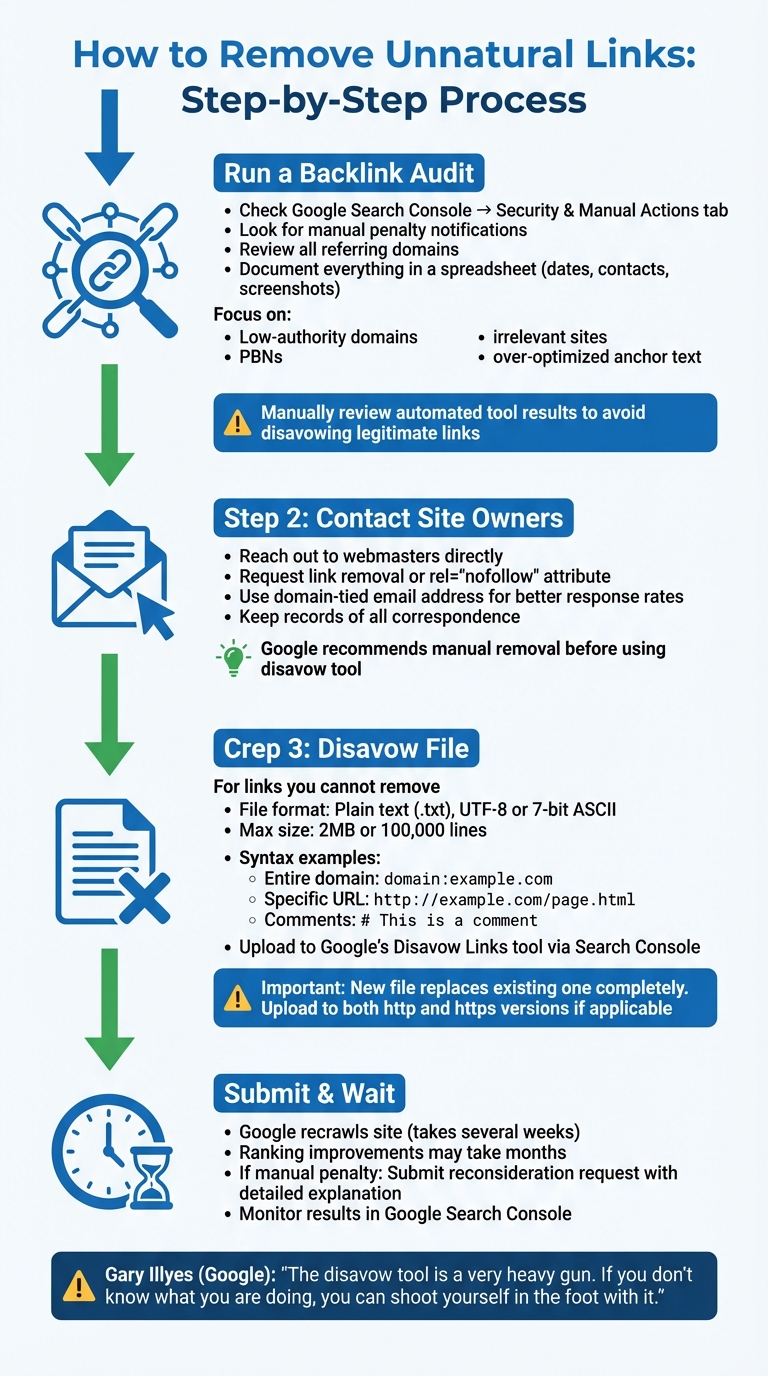
4-Step Process to Remove Unnatural Links and Avoid Google Penalties
Taking action to remove unnatural links is crucial to protect your site’s rankings and maintain compliance with search engine guidelines. Addressing these links quickly can help mitigate penalties – whether algorithmic or manual. The process demands persistence and thorough documentation to meet search engine standards.
Running a Backlink Audit
Start by logging into Google Search Console and checking the "Security & Manual Actions" tab. If Google has flagged your site for unnatural links, you’re dealing with a manual penalty that requires immediate attention. Even if no penalty is present, it’s still important to conduct a detailed review of all referring domains.
Keep a detailed record of your audit process. This includes tracking every step and correspondence in a spreadsheet. For example, in 2013, Pinpoint Designs successfully lifted a manual penalty by documenting their cleanup efforts in a Google Spreadsheet. They included details like contact dates and screenshots of removal requests. Their penalty stemmed from using followed anchor text such as "Web Design Yorkshire" in client website footers.
Pay special attention to links from low-authority domains, Private Blog Networks (PBNs), irrelevant websites, and sources with over-optimized anchor text examples. While automated tools can flag toxic links, it’s essential to manually review these results to avoid disavowing legitimate backlinks by mistake. Google’s Webmaster Trends Analyst, Gary Illyes, cautioned:
"We said multiple times that the disavow tool is a very heavy gun. And if you don’t know what you are doing, you can shoot yourself in the foot with it".
Once the audit is complete, focus on removing or disavowing problematic links.
Removing or Disavowing Bad Links
After identifying harmful links, take immediate steps to address them. Google’s guidelines recommend trying to remove links manually before resorting to the disavow tool. Start by contacting site owners directly and asking them to either delete the link or add a rel="nofollow" attribute. Using an email address tied to your domain can improve your chances of getting a response. Google’s Search Advocate John Mueller has stated:
"If there are some links that you can’t remove yourself, or some that require payment to be removed, then having those in the disavow file is fine as well".
For links that cannot be removed, create a disavow file. This should be a plain text (.txt) file encoded in UTF-8 or 7-bit ASCII, with a maximum size of 2MB or 100,000 lines. Use domain:example.com to disavow an entire site, or specify individual URLs for specific links. You can include comments (lines starting with #) to explain your reasoning – Google ignores these comments, but they can be useful for future reference.
Once your file is ready, upload it to Google’s Disavow Links tool via Search Console. Keep in mind, the tool supports only URL prefix properties, not Domain properties. If your site has both http and https versions, you’ll need to upload the disavow file to each version separately. Remember, submitting a new disavow file will completely replace any existing one, so ensure your file is comprehensive.
It may take several weeks for Google to recrawl your site, and ranking improvements could take months. If you’re dealing with a manual penalty, submit a reconsideration request after uploading your disavow file. Make sure to include a clear explanation of the steps you’ve taken to resolve the issue.
Building a Compliant Backlink Profile
Once you’ve cleaned up your backlink profile, the next step is to focus on creating a penalty-free foundation. This means prioritizing quality, relevance, and diversity to steer clear of the risks associated with manipulative link-building practices.
Prioritize Quality Over Quantity
A single backlink from a respected industry publication can hold far more weight than dozens of links from unrelated, low-quality sites. Here’s a striking fact: over 90% of web pages never rank in search results due to a lack of authoritative backlinks. This highlights the importance of earning editorial placements – links naturally integrated into content by human editors.
When links are embedded in contextually relevant content, they not only enhance the reader’s experience but also signal credibility to search engines. As Matt Cutts, former Head of Webspam at Google, once noted:
"We do reserve the right to treat links in footers a little bit differently… something that’s in an actual paragraph of text is a little more likely to be an editorial link".
To attract these high-value links, create "linkable assets" like original research, in-depth guides, or free tools that journalists and bloggers will naturally want to reference. Aim for backlinks from domains with a Domain Authority (DA) above 40, which serve as strong endorsements of your site’s expertise. Always manually review referring pages to confirm the content is high-quality and the link placement feels natural. You can also leverage AI-powered platforms to streamline your outreach efforts.
Using AI-Powered Platforms Like 3Way.Social
To scale your link-building efforts without cutting corners, tools like 3Way.Social can be a game-changer. This platform uses AI to match domains for contextually relevant links, ensuring compliance with search engine guidelines. Its vetted network helps minimize risks from toxic markers that systems like Google’s SpamBrain are designed to detect.
With 3Way.Social, you can secure permanent do-follow links, avoiding sudden spikes in link acquisition that might trigger spam filters. Since Google’s SpamBrain has been actively identifying manipulative link patterns since 2018, working with platforms that prioritize relevance and quality ensures you’re on the right track. The platform also facilitates guest posting opportunities and flexible exchange options, helping you build a diverse and high-quality backlink profile without resorting to questionable tactics. Pair these efforts with a broad range of link sources to strengthen your profile further.
Diversify Your Link Sources
A robust backlink profile isn’t built from one type of link alone. Instead, include a variety of sources, such as:
- Guest posts
- Editorial citations
- Organic mentions
- Resource page links
- Community references
This diversity signals natural growth to search engines. Additionally, use a mix of anchor text types – branded, naked URLs, and partial-match anchors – while keeping exact-match anchors to a minimum. As Google Search Central explains:
"Good anchor text is descriptive, reasonably concise, and relevant to the page that it’s on and to the page it links to. It provides context for the link, and sets the expectation for your readers".
Consistency is key. Gradual link acquisition over time looks more natural to search engines. Even the best profiles may include 5% to 10% spam links, as search engines understand that no site is immune to low-quality backlinks. However, sudden surges in link volume – without an accompanying PR event or viral content – can raise red flags. To stay compliant, always tag paid links with rel="sponsored" and user-generated content with rel="ugc" as per Google’s guidelines.
Preventing Future Link Problems
Once you’ve cleaned up your link profile and established a solid base, the key to maintaining SEO success lies in staying vigilant. Removing harmful links is just the beginning – keeping your site penalty-free requires ongoing monitoring and dedication to ethical link-building practices.
Monitor Your Backlinks Regularly
Think of monitoring your backlinks like checking your credit report – it needs to be done consistently and carefully. Start with Google Search Console, focusing on the "Security & Manual Actions" tab. If you see a green checkmark with "No issues detected", you’re in good shape. To dig deeper, export your backlink data from GSC and cross-check it with tools like Semrush or Ahrefs. This can help you identify unusual patterns before they escalate.
Make it a habit to conduct a quarterly audit of your backlinks. Watch for unusual spikes in referring domains that don’t align with recent PR campaigns, product launches, or viral moments. These sudden increases could point to manipulative ABC link exchanges or other tactics. Pay close attention to anchor text distribution. If exact-match anchors for specific keywords suddenly climb above 30%-40%, it’s a red flag. Google’s SpamBrain AI, which has been evolving since 2018, is highly adept at catching these patterns – what might have worked years ago won’t pass today.
Here’s a simple framework to guide your monthly backlink checks:
| Indicator | What to Check | Action Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Anchor Text | Percentage of exact-match anchors | Flag if any keyword exceeds 30% |
| Link Velocity | New referring domains per week | Investigate spikes without clear reasons |
| Placement | Links in footers, sidebars, or widgets | Review 20 pages; remove problematic links |
| Relevance | Links from unrelated niches | Flag gambling, pharma, or off-topic sites |
By following this routine, you can catch potential issues early and maintain a clean link profile.
Follow Ethical SEO Practices
Monitoring alone isn’t enough – sticking to ethical link-building practices is just as important. A good rule of thumb: Would this link exist if search engines didn’t? If the answer is "no", it’s likely unnatural. As Dan Fries, Founder of BlueTree, explains:
"The key test: would this link exist if search engines didn’t? If the answer is ‘no,’ it’s likely unnatural".
Focus on building genuine, high-value links. For paid placements, use rel="sponsored", and for user-generated content, apply rel="ugc" – these are essential to comply with Google’s spam policies. Instead of chasing volume, prioritize quality by creating linkable assets like original research, in-depth guides, or free tools. These resources naturally attract editorial mentions. When reaching out for links, always aim for relevance over quantity. A single link from an authoritative, industry-related site is far more impactful than dozens of links from generic directories.
It’s worth noting that unnatural links account for over 75% of all SEO penalties. With Google ramping up enforcement against site reputation abuse and low-quality content as of March 2025, the stakes are higher than ever. By focusing on authentic value and building relationships with reputable publishers, you can safeguard your site’s visibility and ensure steady growth in an ever-changing SEO landscape.
Conclusion
Unnatural links are a leading cause of SEO penalties, accounting for over 75% of cases. The good news? Most of these penalties can be avoided with a well-thought-out approach. By understanding what qualifies as an unnatural link, routinely auditing your backlink profile, and addressing problematic links through removal or disavowal, you can shield your site from the severe traffic losses often highlighted in case studies.
Once your backlink profile is clean, it’s time to focus on sustainable link practices. Shifting from "link building" to "link earning" is more than just a precaution against penalties – it’s a strategy for long-term growth. By developing linkable assets like original research, in-depth guides, or practical tools, you can naturally attract editorial links that strengthen your site’s authority. As Google emphasizes:
"Creating links that weren’t editorially placed or vouched for by the site’s owner on a page, otherwise known as unnatural links, can be considered a violation of our guidelines".
A balanced SEO strategy is key. Tools like 3Way.Social can help you secure and find quality backlinks by connecting with vetted networks and using AI-driven matching to ensure relevance and authenticity. Always use rel="sponsored" for paid placements, vary your anchor text naturally, and conduct regular audits to catch potential issues early.
Google’s SpamBrain AI is constantly evolving, with the latest updates targeting AI-generated link schemes and advanced private blog networks. What worked a few years ago may no longer align with today’s standards. Websites that prioritize genuine value, maintain diverse link sources, and treat backlinks as investments in credibility are the ones that succeed in the long run.
FAQs
How can I tell if I was hit by a manual action or an algorithm update?
To find out if your site has been hit with a manual action, head to Google Search Console. Check for notifications about issues like unnatural links or spam penalties. These are direct actions taken by Google and will be explicitly flagged.
On the other hand, algorithm updates work differently. They usually result in ranking changes without any specific alerts. If you notice sudden drops in traffic or shifts in rankings, it could be a sign that an algorithm update has affected your site.
When should I use Google’s disavow tool instead of trying link removal first?
If your website is dealing with issues like manual actions for unnatural links, involvement in link schemes, or an overwhelming number of spammy backlinks that could flag your site for spam detection, consider using Google’s disavow tool.
That said, always try to remove harmful links manually before turning to the disavow tool. But when manual removal isn’t feasible, the tool can act as a safeguard to help protect your site from potential penalties.
What’s a safe anchor text mix to avoid over-optimized link patterns?
A safe anchor text mix should be balanced, varied, and context-appropriate. Steer clear of overloading with exact match keywords or using excessively long, manipulative anchors. Focus on blending branded, generic, and descriptive anchors to create a natural link profile and avoid the pitfalls of over-optimization.



